- Details
- Written by: Elmazen
- Category: Flags of Countries of the World
- Hits: 1705
Maldives
- Maldives : A Tropical Paradise with a Rich History and Culture,
- Maldives is a small island nation in the Indian Ocean, known for its stunning beaches, coral reefs, and luxury resorts.
- But Maldives is more than just a tourist destination.
Maldives Flag Currency Population Tourism Cities Landmarks History
Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- It has a long and fascinating history, a diverse and vibrant culture, and a dynamic and resilient economy.
- In this article, we will explore some of the aspects that make Maldives a unique and attractive country.
1 - History of Maldives :
- Maldives has been inhabited for over 2,500 years by various peoples, including Buddhists, Hindus, Arabs, Persians, and Africans.
- The first recorded history of Maldives dates back to the 12th century, when it was ruled by a series of sultans who adopted Islam as the official religion.
- Maldives was also a strategic trading hub in the Indian Ocean, connecting Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- Maldives was influenced by various cultures and civilizations, such as India, Sri Lanka, China, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Oman.
- Maldives became a British protectorate in 1887, but retained its autonomy and sovereignty.
- It gained full independence in 1965, and became a republic in 1968.
- Since then, Maldives has faced several challenges and changes, such as political instability, environmental threats, social reforms, and economic development.
- Maldives has also played an active role in regional and international affairs, especially in promoting peace and cooperation among Islamic countries.
2 - Capital of Maldives :
- The capital of Maldives is Malé, which is also the largest and most populous city in the country.
- Malé is located on a small island in the North Male Atoll, and covers an area of about 6 square kilometers.
- It is one of the most densely populated cities in the world, with over 200,000 people living in a limited space.
- Malé is the political, economic, cultural, and educational center of Maldives.
- It hosts the government offices, the parliament, the president’s residence, the airport, the port,
- the university, the national museum, the Islamic center,
- and many other landmarks and facilities.
- Malé is also a vibrant and modern city that offers a variety of attractions and activities for visitors.
- You can enjoy the scenic views of the ocean from the artificial beach or the waterfront park;
- you can explore the historical and religious sites such as the Old Friday Mosque or the Grand Friday Mosque;
- you can shop for local handicrafts and souvenirs at the markets or the shopping malls;
- you can taste the delicious cuisine and nightlife at the restaurants or the cafes;
- or you can simply relax and unwind at one of the many spas or hotels.
3 - Maldives Country Flag Meaning :
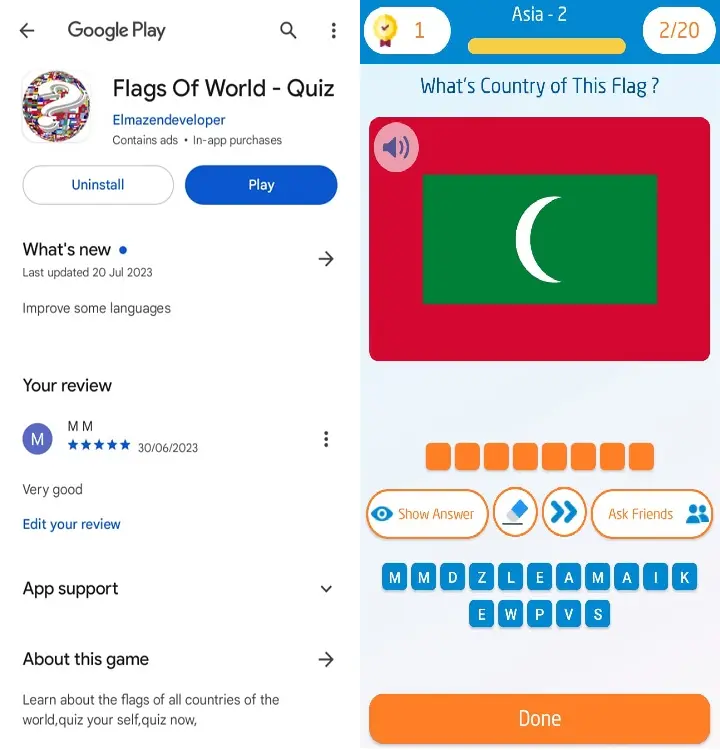
- The national flag of Maldives consists of three colors : red, green, and white.
- The flag has a red background with a green rectangle in the center that contains a white crescent moon.
- Each color has a symbolic meaning that reflects the identity and values of Maldives.
- The red color represents the bloodshed and bravery of the heroes who sacrificed their lives for the nation.
- It also symbolizes the traditional red flag that was used by many Arab traders and sailors who visited Maldives in the past.
- The green color represents the wealth and prosperity of Maldives.
- It also symbolizes the lush vegetation and nature that surrounds the islands.
- The white crescent moon represents Islam, which is the official religion and faith of Maldives.
- It also symbolizes peace and harmony among the people.
- Maldives Country Belongs to Which Continent ?
4 - Maldives belongs to the continent of Asia.
- Asia is the largest and most populous continent on Earth.
- It covers about 30% of the land area and 60% of the population of the world.
- Asia is home to many diverse cultures, languages, religions, histories, geographies, climates, and natural resources.
- Maldives is located in South Asia, which is one of the subregions of Asia.
- South Asia comprises eight countries : Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
- South Asia has a population of about 1.9 billion people, which is about one-fourth of the world’s population.
- South Asia is also known for its rich cultural heritage, ancient civilizations, and influential religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, and Sikhism.
5 - Maldives Country Economy :
- Maldives has a small but growing economy that is based on tourism, fishing, and services.
- Tourism is the main source of income and foreign exchange for Maldives.
- It accounts for about 28% of the gross domestic product (GDP) and employs about 20% of the labor force.
- Maldives attracts millions of visitors every year who come to enjoy its pristine beaches, crystal clear waters, and exotic resorts.
- Maldives offers a range of tourism products, such as luxury hotels, water villas, spa treatments, diving, snorkeling, surfing, sailing, fishing, and cultural tours.
- Fishing is the second largest sector of the economy and the main livelihood for many Maldivians.
- It accounts for about 10% of the GDP and employs about 11% of the labor force.
- Maldives has a rich and diverse marine life, with over 1,000 species of fish, including tuna, grouper, snapper, shark, and reef fish.
- Maldives exports most of its fish products to Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
- Services is the third largest sector of the economy and the fastest growing one.
- It accounts for about 18% of the GDP and employs about 23% of the labor force.
- Services include transportation, communication, banking, insurance, health, education, and public administration.
- Maldives has invested in improving its infrastructure, technology, and human capital to enhance its service delivery and competitiveness.
6 - Maldives Country Currency :
- The official currency of Maldives is the Maldivian Rufiyaa (MVR), which is divided into 100 laari.
- The rufiyaa was introduced in 1947, replacing the Ceylonese rupee that was previously used.
- The rufiyaa is issued by the Maldives Monetary Authority (MMA), which is the central bank of Maldives.
- The rufiyaa is pegged to the US dollar at a fixed rate of 15.42 rufiyaa per dollar.
- The rufiyaa comes in both banknotes and coins.
- The banknotes are in denominations of 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 500, and 1000 rufiyaa.
- The coins are in denominations of 1, 2, 5, 10, 25, and 50 laari, and 1 and 2 rufiyaa.
- The banknotes and coins feature various symbols and images that represent the history, culture, and nature of Maldives.
- The rufiyaa is not widely accepted outside Maldives and is not easily exchangeable in other countries.
- Therefore, most tourists use foreign currencies such as US dollars or euros to pay for their expenses in Maldives.
- Most hotels, resorts, shops, and restaurants accept foreign currencies or credit cards as payment methods.
- However, some small businesses or local vendors may only accept rufiyaa or may charge a higher rate for foreign currencies.
- Therefore, it is advisable to have some rufiyaa on hand for small purchases or tips.
7 - Maldives Country Code :
- The country code for Maldives is +960.
- This is the international dialing code that you need to use when you are calling Maldives from another country.
- You also need to add the area code and the local number of the person or place you are calling.
- The area codes for Maldives are two digits long and start with a zero.
- They indicate the geographic region or island where the phone number is located.
- For example, the area code for Male is 03; the area code for Addu City is 06; and the area code for Hulhumale is 09.
- The local numbers for Maldives are seven digits long and start with either a seven or a nine.
- They indicate the specific phone line or mobile network that belongs to the person or place you are calling.
- For example, if you want to call a hotel in Male from the US or Canada, you need to dial :
011 + 960 + 03 + local number.
- 011 is the exit code for North America; 960 is the country code for Maldives; 03 is the area code for Male; and local number is the seven-digit number of the hotel.
8 - How to Pronounce Maldives Country :
- Maldives is pronounced as /ˈmɔːldiːvz/ (MOHL-deevz) in British English and /ˈmældaɪvz/ (MAL-dyvz) in American English.
- The stress is on the first syllable in both cases.
- The first syllable sounds like “mole” in British English and “mall” in American English.
- The second syllable sounds like “deev” in British English and “dyve” in American English.
- The final sound is a voiced “z” sound that vibrates your vocal cords.
9 - Maldives Country Abbreviation :
- The official abbreviation for Maldives is MV.
- This is based on the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 standard that assigns two-letter codes to countries and territories.
- MV stands for Maldive Islands, which is an alternative name for Maldives.
- Some other abbreviations that are sometimes used for Maldives are :
- MLD : This is based on the ISO 3166-1
Maldives Flag Currency Population Tourism Cities Landmarks History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- Maldives has many landmarks that showcase its natural beauty, cultural heritage, and historical significance.
- Some of the landmarks that you can visit in Maldives are :
10 - Tsunami Monument : This is a memorial that honors the victims of the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami that devastated Maldives and other countries.
- The monument consists of a steel sphere with vertical rods that represent the 26 atolls of Maldives and the lives lost in each one.
- The monument is located in Male, near the artificial beach and the waterfront park.
- You can learn more about the tsunami and its impact on Maldives at the nearby National Museum.
11 - Hulhumale Beach : This is one of the most popular beaches in Maldives, located on the island of Hulhumale,
- which is an artificial island created to accommodate the growing population and development of Maldives.
- The beach is known for its white sand, turquoise water, and palm trees.
- You can enjoy various activities on the beach, such as swimming, snorkeling, sunbathing, or relaxing.
- You can also find many hotels, restaurants, and shops near the beach.
12 - Grand Friday Mosque : This is the largest and most impressive mosque in Maldives, located in Male.
- The mosque was built in 1984 and can accommodate up to 5,000 worshippers.
- The mosque has a golden dome, a minaret, and a marble facade that reflect the Islamic architecture and art of Maldives.
- The mosque also houses the Islamic Center, which is a complex that includes a library, a conference hall, an auditorium, and a religious school.
Maldives Flag Currency Population Tourism Cities Landmarks History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- Maldives is a country that consists of many islands, some of which are classified as cities.
- A city in Maldives is an island that has a population of more than 25,000 people and meets certain criteria of urbanization and development.
- There are currently six cities in Maldives : Male, Fuvahmulah, Addu, Kulhudhuffushi, Thinadhoo, and Hithadhoo.
- Each city has its own attractions and features that make it worth visiting.
- Here are some brief descriptions of the cities in Maldives :
- Malé :
13 - Male : Male is the capital and the largest city of Maldives.
- It is located on a small island in the North Male Atoll and covers an area of about 6 square kilometers.
- It is one of the most densely populated cities in the world, with over 200,000 people living in a limited space.
- Male is the political, economic, cultural, and educational center of Maldives.
- It hosts the government offices, the parliament, the president’s residence, the airport, the port,
- the university, the national museum, the Islamic center, and many other landmarks and facilities.
- Male is also a vibrant and modern city that offers a variety of attractions and activities for visitors.
- You can enjoy the scenic views of the ocean from the artificial beach or the waterfront park;
- you can explore the historical and religious sites such as the Old Friday Mosque or the Grand Friday Mosque;
- you can shop for local handicrafts and souvenirs at the markets or the shopping malls;
- you can taste the delicious cuisine and nightlife at the restaurants or the cafes;
- or you can simply relax and unwind at one of the many spas or hotels.
- Fuvahmulah :
14 - Fuvahmulah : Fuvahmulah is the second largest city and the only one-island atoll in Maldives.
- It is located in the southern part of Maldives and covers an area of about 12 square kilometers.
- It has a population of about 12,000 people who speak a distinctive dialect of Dhivehi.
- Fuvahmulah is known for its natural beauty and diversity.
- It has a tropical forest, a freshwater lake, a marshland, a pebble beach, a black sand beach, and a white sand beach.
- It also has a rich marine life, with over 300 species of fish, including sharks, rays, turtles, dolphins, and whales.
- Fuvahmulah is a paradise for nature lovers and adventure seekers.
- You can enjoy various activities such as hiking, biking, fishing, diving, snorkeling, surfing, or whale watching.
- Addu City :
15 - Addu : Addu is the third largest city and the southernmost atoll in Maldives.
- It is composed of six inhabited islands that are connected by causeways.
- It has a population of about 35,000 people who have a distinct culture and history from other Maldivians.
- Addu was once a British naval base during World War II and later became a stronghold of opposition to the central government.
- Addu has many historical and cultural attractions such as the Gan International Airport, which was built by the British;
- the Equatorial Convention Center, which hosted the 17th SAARC summit in 2011;
- the Addu Museum, which displays artifacts and photos from different eras; and the Koagannu Cemetery, which is the oldest cemetery in Maldives.
- Addu also has many natural attractions such as the Addu Nature Park, which is home to various birds and animals;
16 - the Hithadhoo Protected Area, which is a mangrove forest; and the Shangri-La’s Villingili Resort & Spa, which is a luxury resort on a private island.
Maldives Flag Currency Population Tourism Cities Landmarks History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- There are many beautiful beaches in Maldives that you can visit and enjoy.
- Some of them are :
17 - Mudhdhoo Beach : This beach is famous for its bioluminescent plankton that glow in the dark and create a magical effect on the sand.
- You can see this phenomenon on some nights, especially during the new moon.
- This beach is also part of the Baa Atoll Biosphere Reserve, which is a Unesco-protected area that hosts a rich marine life.
18 - Cocoa Island : This island is also known as Makunufushi and is home to a luxurious resort called COMO Cocoa Island.
- The island has a long sandbar that extends into the ocean and offers stunning views of the turquoise water.
- The island also has two coral reefs that are ideal for snorkeling and diving.
19 - Banyan Tree Vabbinfaru : This island is located near the capital Malé and has a circular beach that surrounds a large lagoon.
- The beach is perfect for relaxing, swimming, and sunbathing.
- The lagoon also has a coral reef that attracts many fish, turtles, and sharks.
- You can snorkel or dive in the lagoon and explore the underwater world.
20 - Dhigurah Island : This island is one of the longest islands in Maldives and has a white-sand beach that stretches for about 3 kilometers.
- The beach is also a nesting site for sea turtles, especially green turtles and hawksbill turtles.
- You can watch them lay their eggs or hatch on the beach at night.
- The island also has a whale shark point where you can see these gentle giants swimming in the water.
21 - Bikini Beach, Maafushi Island : This beach is one of the few public beaches in Maldives where you can wear a bikini or swimwear without any restrictions.
- The beach is located on Maafushi Island, which is one of the most popular local islands in Maldives.
- The beach has soft sand, clear water, and palm trees.
- You can also find many cafes, shops, and guesthouses near the beach.
Maldives Flag Currency Population Tourism Cities Landmarks History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
22 - The climate in Maldives is tropical, which means it is hot and humid all year round, but with different seasons of rainfall and sunshine.
- The best time to visit Maldives depends on your preferences and activities,
- but generally speaking, the dry season from December to April is more suitable for sunbathing, diving, and snorkeling,
- while the wet season from May to October is more suitable for surfing, sailing, and fishing.
- Here are some more details about the climate in Maldives :
- The average temperature in Maldives is around 28 °C (83 °F), with little variation throughout the year.
- The hottest month is April, when the temperature can reach 32 °C (90 °F), and the coldest month is December, when the temperature can drop to 25 °C (77 °F).
- The average rainfall in Maldives is around 2,000 mm (79 inches) per year, with most of it falling during the wet season.
- The wettest month is October, when the rainfall can reach 230 mm (9 inches), and the driest month is February, when the rainfall can drop to 50 mm (2 inches).
- The average sunshine in Maldives is around 7 hours per day, with more hours of sunshine during the dry season.
- The sunniest month is February, when the sunshine can reach 10 hours per day, and the cloudiest month is September, when the sunshine can drop to 5 hours per day.
- The average sea temperature in Maldives is around 28 °C (82 °F), which is warm and pleasant for swimming and water sports.
- The sea temperature does not vary much throughout the year, but it can be slightly cooler in January and February, and slightly warmer in April and May.
- The average wind speed in Maldives is around 6 mph (10 km/h), with stronger winds during the wet season.
- The windiest month is May, when the wind speed can reach 9 mph (14 km/h), and the calmest month is November, when the wind speed can drop to 4 mph (6 km/h).
- The average humidity in Maldives is around 80%, which can make the air feel muggy and sticky.
- The humidity does not vary much throughout the year, but it can be slightly higher in May and June, and slightly lower in January and February.
23 - Maldives is an island country that does not share any land borders with other countries.
- It is surrounded by the Indian Ocean and lies south of India and Sri Lanka.
- Maldives consists of about 1,190 coral islands that are grouped into 26 atolls, which are ring-shaped coral reefs that enclose a lagoon.
- The islands of Maldives are very small and low-lying, with an average elevation of only 1.5 meters above sea level.
- Maldives has a total land area of 298 square kilometers, making it the smallest country in Asia by both land area and population.
24 - Maldives has a maritime border with India, which is defined by a bilateral agreement signed in 1976.
- The agreement establishes the boundary line between the two countries based on the median line principle,
- which means that the border is equidistant from the nearest points on the baselines of both countries.
- The agreement also defines the exclusive economic zones (EEZs) of both countries, which extend up to 200 nautical miles from their respective baselines.
- The EEZs are areas where each country has sovereign rights over the exploration and use of marine resources.
25 - Maldives also has a maritime border with Sri Lanka, which is defined by a bilateral agreement signed in 1979.
- The agreement establishes the boundary line between the two countries based on the equidistance principle,
- which means that the border is equidistant from the nearest points on the coastlines of both countries.
- The agreement also defines the continental shelves of both countries,
- which extend up to 200 nautical miles from their respective coastlines or to the outer edge of the continental margin, whichever is greater.
- The continental shelves are areas where each country has sovereign rights over the exploration and use of natural resources on or under the seabed .
26 - Maldives also has a maritime border with the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT),
- which is an overseas territory of the United Kingdom that comprises the Chagos Archipelago and its surrounding waters.
- The BIOT lies to the south of Maldives and is administered from London.
- The maritime border between Maldives and BIOT is not clearly defined or agreed upon by both parties.
- There have been disputes and negotiations over the delimitation of the border and the sovereignty of some islands and reefs in the area .
Maldives Flag Currency Population Tourism Cities Landmarks History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
National Anthem of Maldives
- Details
- Written by: Elmazen
- Category: Flags of Countries of the World
- Hits: 1582
Malaysia
Malaysia: A Diverse and Dynamic Destination,
1 - Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia, lying just north of the Equator.
- that is composed of two noncontiguous regions:
Malaysia Flag Currency Tourism Population Cities Landmarks History
Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- Peninsular Malaysia, which is on the Malay Peninsula, and East Malaysia, which is on the island of Borneo.
2 - Malaysia has a population of over 33 million people.
- with a diverse ethnic, cultural, and religious composition The majority of Malaysians are Muslims,
- but there are also significant minorities of Buddhists, Christians, Hindus, and others Malaysia is a federal constitutional monarchy,
- with a parliamentary system of government and a Yang di-Pertuan Agong (monarch) as the head of state.
- Malaysia has a rich and complex history, dating back to ancient times when it was part of various kingdoms and empires, such as Srivijaya, Majapahit, Malacca,
- and Johor Malaysia was colonized by the Portuguese, the Dutch, and the British,
who brought their influences to the region Malaysia also faced Japanese occupation during World War II, and a communist insurgency during the Malayan Emergency,
- Malaysia gained its independence from Britain in 1957 as the Federation of Malaya,
- and later expanded to include Singapore, Sabah, and Sarawak in 1963 as Malaysia However,
- Singapore left the federation in 1965 due to political and racial tensions Since then,
- Malaysia has undergone rapid economic and social development,
- becoming one of the most prosperous and dynamic countries in Asia
3 - The capital of Malaysia is Kuala Lumpur, which is also the largest city and the cultural, commercial,
- and transportation center of the country Kuala Lumpur is famous for its modern skyline,
- dominated by the Petronas Twin Towers,
- which are the tallest twin buildings in the world Kuala Lumpur also offers a variety of attractions,
- such as historical monuments, museums, parks, shopping malls, and nightlife venues Kuala Lumpur is.
4 - pronounced as /kʊələ ˈlʊmpʊə/ in British English and /kʊɑlə ˈlʊmpʊr/ in American English.
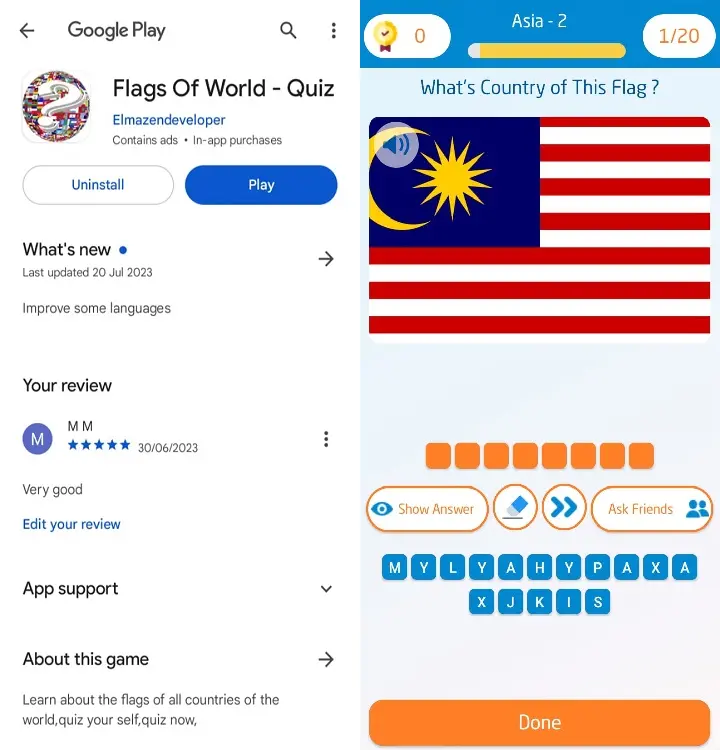
5 - The flag of Malaysia consists of 14 horizontal stripes of red and white alternating with a blue canton bearing a yellow crescent
and a 14-pointed star The flag is often referred to as Jalur Gemilang (Stripes of Glory) in Malay The 14 stripes represent the equal status of the 13 states
and the federal territories in the federation,
while the 14 points of the star symbolize the unity among them The crescent represents Islam as the official religion of the country,
while the yellow color signifies the royal color of the Malay rulers The blue canton indicates the unity of the Malaysian people
6 - Malaysia belongs to the continent of Asia,
- which is the largest and most populous continent in the world Malaysia is located in Southeast Asia,
- which is a subregion of Asia that consists of 11 countries:
Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Timor-Leste, and Vietnam,
Southeast Asia is known for its cultural diversity, tropical climate, natural beauty, and historical heritage,
7 - Malaysia has a strong and diversified economy that ranks among the upper middle-income countries in the world,
- Malaysia’s economy is based on various sectors such as manufacturing, services, tourism, agriculture, mining, and oil and gas,
- Malaysia is also one of the leading exporters of palm oil, rubber, electronics, petroleum products,
and medical devices,
- Malaysia’s economy has been growing steadily since its independence in 1957 with an average annual growth rate of 5.4% since 2010.
- Malaysia is expected to achieve its transition from an upper middle-income economy to a high-income economy by 2024.
8 - The currency of Malaysia is the Malaysian ringgit (MYR), which is divided into 100 sen (cents).
- The word ringgit means “jagged” in Malay and refers to the serrated edges of Spanish silver coins that circulated in the region in the past.
- The currency symbol for ringgit is RM (Ringgit Malaysia), while the currency code for ringgit is MYR.
- The exchange rate of ringgit to US dollar of October 14, 2023 is 1 USD = 4.73 MYR.
9 - The country code for Malaysia is +60, which is used to make international phone calls to Malaysia from other countries.
- The country code is followed by the area code and the local phone number.
- For example, to call a landline in Kuala Lumpur from the United States, one would dial 011 + 60 + 3 + local number.
- To call a mobile phone in Malaysia from the United States, one would dial 011 + 60 + 1 + local number.
10 - The abbreviation for Malaysia is MY or MYS, which are the two-letter and three-letter country codes respectively according to the ISO 3166-1 standard.
- These codes are used for various purposes such as internet domain names, vehicle registration plates, and sports teams.
- For example, the internet domain name for Malaysia is .my, the vehicle registration plate for Malaysia is MY, and the Olympic code for Malaysia is MAS.
11 - The culture of Malaysia is influenced by the diverse ethnic, religious, and historical backgrounds of its people.
- Malaysia is known for its multiculturalism and tolerance, where different groups coexist peacefully and celebrate each other’s festivals and traditions.
- Some of the major cultural aspects of Malaysia are its cuisine, music, art, literature, architecture, clothing, and languages.
- Malaysia has many best places to visit for tourists who want to experience its natural beauty, cultural diversity, and historical heritage.
- Some of the most popular destinations in Malaysia are:
12 - Penang Island: A UNESCO World Heritage Site that offers a blend of colonial architecture, street art, multicultural cuisine, and sandy beaches.
13 - Langkawi: An archipelago of 99 islands that features tropical rainforests, waterfalls, mangroves, wildlife parks, and duty-free shopping.
14 - Malacca: A historic city that showcases the influences of Malay, Chinese, Portuguese, Dutch,
and British cultures in its buildings, museums, temples, churches, and forts.
15 - Kota Kinabalu: The capital of Sabah state that serves as a gateway to explore the natural wonders of Mount Kinabalu,
Kinabalu National Park, Tunku Abdul Rahman Marine Park, and Sepilok Orangutan Rehabilitation Centre.
16 - Kuching: The capital of Sarawak state that offers a glimpse of the diverse ethnic groups of Borneo in its cultural villages, museums, markets, and festivals.
17 - Kuala Lumpur: The vibrant and modern capital of Malaysia that boasts of iconic landmarks
such as the Petronas Twin Towers, KL Tower, Batu Caves, Merdeka Square, and Central Market.
- These are just some of the many attractions that Malaysia has to offer to visitors who want to discover its charm and diversity.
- Malaysia is truly a destination that has something for everyone.
Malaysia Flag Currency Tourism Population Cities Landmarks History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- Some of the landmarks in Malaysia that you might be interested in visiting.
- Some additional details about four of them:
18 - Mount Kinabalu: This is the highest mountain in Malaysia and the third highest in Southeast Asia,
- with an elevation of 4,095 meters above sea level It is located in Sabah, East Malaysia,
- and is part of the Kinabalu National Park, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site Mount Kinabalu is known for its rich biodiversity,
- with over 5,000 species of plants and animals, including many endemic and rare species It is also a popular destination for hiking and climbing enthusiasts,
-who can challenge themselves to reach the summit or enjoy the scenic trails and views along the way
19 - Melaka Sultanate Palace: This is a replica of the original palace of the Malacca Sultanate,
- which was one of the most powerful and influential kingdoms in Southeast Asia from the 15th to the 16th century.
- The palace was built in 1985 using traditional Malay architecture and craftsmanship, without using any nails or screws.
- It houses the Malacca Cultural Museum, which displays various artifacts and exhibits related to the history and culture of Malacca and the Malay people.
- The palace is surrounded by a beautiful garden and a moat, and is located near other historical landmarks such as St. Paul’s Hill and A Famosa Fort.
20 - Pulau Tioman: This is an island off the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia, in the state of Pahang.
- It is part of the Mersing Marine Park, which consists of nine islands that are protected for their marine life and coral reefs.
- Pulau Tioman is famous for its pristine beaches, clear waters, and tropical forests.
- It offers various activities for visitors such as snorkeling, diving, surfing, kayaking, hiking, and wildlife watching.
- It is also home to several villages and resorts that cater to different budgets and preferences.
21 - Khoo Kongsi Clanhouse: This is a grand and ornate building that serves as the ancestral hall of the Khoo clan, one of the prominent Chinese families in Penang.
- It was built in 1906 by the descendants of Khoo Kongsi, who migrated from China to Malaya in the 17th century.
- The clanhouse showcases the exquisite craftsmanship and artistry of Chinese architecture, with intricate carvings, paintings, sculptures, and lanterns.
- It also features a museum that displays the history and heritage of the Khoo clan and their contributions to Penang’s society and economy.
Malaysia Flag Currency Tourism Population Cities Landmarks History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- Malaysia is a country that has many cities, each with its own unique features and attractions.
- Some more details about four of the cities in Malaysia that you might want to know more about:
22 - George Town: This is the capital city of Penang, a state in the northwest of Peninsular Malaysia.
- George Town is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, as it has a rich and diverse cultural heritage, influenced by Malay, Chinese, Indian, British, and other communities.
- George Town is famous for its street food, street art, colonial architecture, temples, mosques, churches, and museums.
- Some of the popular tourist attractions in George Town are Kek Lok Si Temple, Cheong Fatt Tze Mansion, Penang Peranakan Museum, and Fort Cornwallis.
- George Town has a population of about 794,313 people as of 2020.
23 - Kota Kinabalu: This is the capital city of Sabah, a state in the northeast of Borneo.
- Kota Kinabalu serves as a gateway to explore the natural wonders of Sabah,
- such as Mount Kinabalu, Kinabalu National Park, Tunku Abdul Rahman Marine Park, and Sepilok Orangutan Rehabilitation Centre.
- Kota Kinabalu also offers a variety of cultural and historical attractions,
- such as the Atkinson Clock Tower, the Sabah State Museum, the Mari Mari Cultural Village, and the Kota Kinabalu City Mosque.
- Kota Kinabalu has a population of about 349,147 people as of 2020.
24 - Ipoh: This is the capital city of Perak, a state in the west of Peninsular Malaysia.
- Ipoh is known for its natural beauty, as it is surrounded by limestone hills and caves.
- Ipoh is also famous for its cuisine, especially its white coffee, bean sprouts chicken, and dim sum.
- Ipoh has many historical and cultural landmarks, such as the Ipoh Railway Station, the Birch Memorial Clock Tower, the Concubine Lane, and the Han Chin Pet Soo Museum.
- Ipoh has a population of about 759,952 people as of 2020.
25 - Kuching: This is the capital city of Sarawak, a state in the northwest of Borneo.
- Kuching is the largest city in Borneo and one of the most multicultural cities in Malaysia.
- Kuching has a rich and varied history, as it was once ruled by the Bruneian Empire,
- the White Rajahs of Sarawak, the Japanese occupation, and the British colonial administration.
- Kuching has many attractions that showcase its diversity and heritage,
- such as the Sarawak Museum, the Astana Palace, the Kuching Waterfront, and the Cat Museum.
- Kuching has a population of about 325,132 people as of 2020.
Malaysia Flag Currency Tourism Population Cities Landmarks History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- Malaysia has many beautiful and diverse beaches that cater to different types of travelers.
- Whether you are looking for a relaxing getaway, a fun-filled adventure, or a cultural immersion,
- Some more details about some of the beaches in Malaysia that you might want to know more about:
26 - Desaru Beach: This is one of the most popular beaches in Malaysia, as it is easily accessible from Singapore by ferry.
- Desaru Beach is located in Johor, on the southeast coast of Peninsular Malaysia.
- It offers a long stretch of golden sand, clear blue water, and various activities such as water sports, golf, and spa.
- Desaru Beach is also home to several resorts and hotels that cater to different budgets and tastes
27 - Pantai Air Papan: This is a low-key and peaceful beach in Mersing, Johor, on the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia.
- Pantai Air Papan is ideal for those who want to escape the crowds and enjoy the natural scenery.
- The beach has soft white sand, calm water, and lush greenery.
- There are also some small eateries nearby that serve local delicacies such as nasi lemak and mee rebus.
- Pantai Air Papan is also a good base to explore the nearby islands and marine parks by boat.
28 - Pantai Cenang Beach: This is the most lively and vibrant beach in Langkawi, an island off the northwest coast of Peninsular Malaysia.
- Pantai Cenang Beach is famous for its nightlife, as it has many seaside bars, restaurants, and clubs that offer live music, fire shows, and parties.
- The beach also has a wide range of water sports, such as jet skiing, parasailing, and banana boating.
- Pantai Cenang Beach is also close to other attractions in Langkawi, such as the Underwater World aquarium, the Rice Museum, and the Cenang Mall
29 - Tengkorak Beach: This is a hidden gem in Langkawi, located at the northern tip of the island.
- Tengkorak Beach is a small and secluded beach that offers a tranquil and idyllic setting for a picnic or a swim.
- The beach has fine white sand, clear turquoise water, and shady palm trees.
- There are also some beach huts that provide shelter and facilities for visitors.
- Tengkorak Beach is also near the Crocodile Adventureland and the Oriental Village, where you can take the cable car to the Sky Bridge.
Malaysia Flag Currency Tourism Population Cities Landmarks History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
30 - Malaysia has a tropical climate, which means that it is hot, humid, and rainy throughout the year.
- The average temperature is around 25 °C (77 °F), and there is little variation between seasons.
- However, Malaysia experiences two monsoon seasons, which affect the rainfall patterns and the wind direction.
- The northeast monsoon lasts from November to March, and brings heavy rain to the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia and the north-east coast of Borneo.
- The southwest monsoon lasts from May to September, and brings less rain but more wind to the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia and the south-west coast of Borneo.
- Between the monsoons, there are intermonsoonal periods, which are usually drier and calmer.
- The rainfall in Malaysia is generally high, ranging from 2,000 to 3,000 mm (79 to 118 in) per year in most areas.
- The sun shines for about 4 to 6 hours a day on average, depending on the cloud cover and the location.
- Malaysia’s climate is influenced by various factors, such as its proximity to the Equator,
- its maritime location, its topography, and its exposure to different airstreams.
- Malaysia’s climate also varies according to the altitude, as the temperature decreases by about 0.6 °C (1 °F) for every 100 meters (330 feet) of elevation.
- Therefore, the highlands and mountains in Malaysia have a cooler and wetter climate than the lowlands and coastal areas.
31 - Malaysia is a country that has both land and maritime borders with several other countries in Southeast Asia.
- Some more details about Malaysia’s borders:
- Malaysia’s total land border length is 3,147.3 km, which is divided into two parts: Peninsular Malaysia and East Malaysia
- Peninsular Malaysia shares a land border with Thailand to the north, Singapore to the south, and Indonesia and Vietnam to the east.
- The border with Thailand is 646.5 km long, the border with Singapore is 1.2 km long, and the border with Indonesia and Vietnam is 506 km long.
- East Malaysia shares a land border with Brunei, Indonesia, and the Philippines to the north, and Indonesia and Vietnam to the south.
- The border with Brunei is 481.3 km long, the border with Indonesia is 2,019.5 km long, and the border with the Philippines is 22.8 km long.
- Malaysia’s total maritime boundary length is 4,675 km, which is also divided into two parts: Peninsular Malaysia and East Malaysia.
- Peninsular Malaysia has maritime boundaries with Thailand, Indonesia, Singapore, and Vietnam in the Straits of Malacca, the Gulf of Thailand, and the South China Sea.
- Some of these boundaries have been delimited through agreements with the neighboring countries, while others are still subject to disputes or negotiations.
- East Malaysia has maritime boundaries with Brunei, Indonesia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Vietnam in the South China Sea and the Sulu Sea.
- Some of these boundaries have been delimited through agreements or joint development arrangements with the neighboring countries,
- while others are still subject to disputes or negotiations
Malaysia Flag Currency Tourism Population Cities Landmarks History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
National Anthem of Malaysia
- Details
- Written by: Elmazen
- Category: Flags of Countries of the World
- Hits: 2201
India
India is a country that fascinates many travelers with its diversity, culture, and history.
1 - India is the second most populous country in the world, with over 1.4 billion people, and the seventh largest by area.
- India is also one of the oldest civilizations in the world, with a rich heritage that spans thousands of years.
India Flag Population Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism History
Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
2 - India’s capital is New Delhi, which is home to many iconic landmarks such as the Red Fort, the Qutub Minar, and the India Gate.
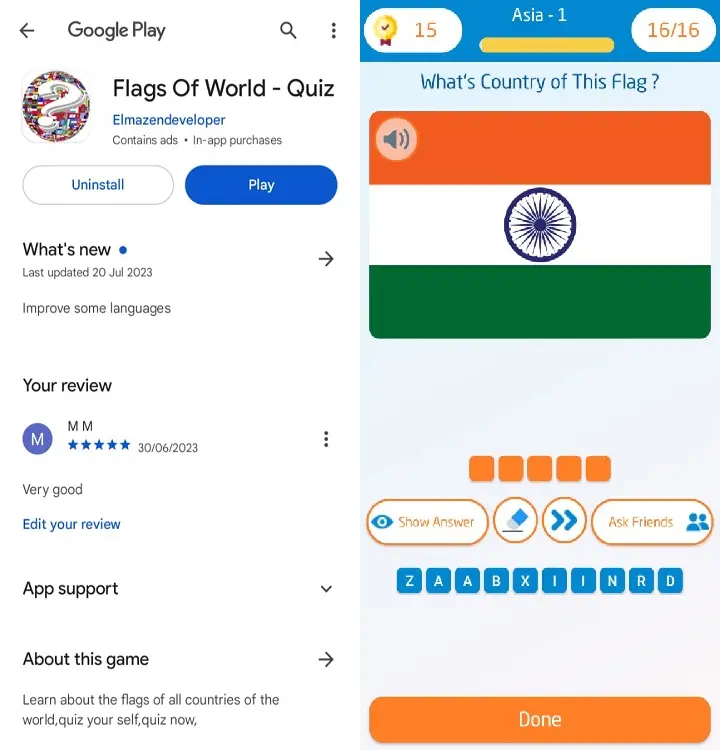
3 - India’s national flag is a horizontal tricolor of saffron, white, and green, with a 24-spoke wheel called the Ashok Chakra in the center.
The saffron represents courage and sacrifice, the white represents peace and truth,
the green represents prosperity and faith, and the wheel represents the cycle of life and motion.
4 - India belongs to the continent of Asia, and shares borders with Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Myanmar.
- India also has a long coastline along the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Indian Ocean.
5 - India’s economy is one of the fastest-growing in the world, with a GDP of $3.75 trillion in 2023.
- India is a major exporter of information technology services, business outsourcing services, and software workers.
- India also has a large agricultural sector, producing crops such as rice, wheat, cotton, tea, and spices.
6 - India’s currency is the Indian rupee (INR), which is divided into 100 paisa.
- The exchange rate in 12 October 2023 was 1 USD = 83.3 INR.
7 - India’s country code is +91, and its internet domain is .in.
8 - To pronounce India correctly, you can say it as /ˈɪn.di.ə/ in British English or /ˈɪn.di.ə/ in American English.
9 - The abbreviation for India is IND.
10 - India’s culture is a blend of various traditions, religions, languages, and arts.
- India is known for its diversity and tolerance, as it hosts many faiths such as Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, and Jainism.
11 - India has 22 official languages and hundreds of dialects spoken across the country.
- Some of the most widely spoken languages are Hindi, English, Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil, Urdu, and Gujarati.
- India also has a rich literary and artistic heritage, producing works such as the Vedas, the Ramayana, the Mahabharata, the Taj Mahal, and Bollywood movies.
- India has many tourist attractions that appeal to different types of travelers.
- Whether you are looking for historical monuments, natural wonders, spiritual sites, or cultural experiences, India has something for everyone.
- some of the best places to visit in India:
12 - Agra: Agra is famous for being the home of the Taj Mahal, one of the Seven Wonders of the World and a symbol of love and beauty.
- The Taj Mahal is a white marble mausoleum built by Mughal emperor Shah Jahan for his beloved wife Mumtaz Mahal in the 17th century.
- Agra also has other attractions such as Agra Fort, Fatehpur Sikri, and Mehtab Bagh.
13 - Goa: Goa is a state in western India that is known for its beaches, nightlife, and Portuguese influence.
- Goa was a colony of Portugal until 1961 and still retains some of its architecture, cuisine, and culture.
- Goa is a popular destination for sun-seekers, party-goers, and adventure-lovers.
14 - Delhi: Delhi is the capital of India and a city that showcases the contrast between old and new.
- Delhi has many historical sites such as Red Fort, Qutub Minar, Humayun’s Tomb, Jama Masjid, and Raj Ghat.
- Delhi also has modern attractions such as Lotus Temple, Akshardham Temple, India Gate, Connaught Place, and Chandni Chowk.
15 - Jaipur: Jaipur is the capital of Rajasthan and a city that exudes royal charm and elegance.
- Jaipur is also known as the Pink City because of its pink-colored buildings that were painted to welcome King Edward VII in 1876.
- Jaipur has many palaces, forts, temples, museums, and markets that reflect its rich culture and history.
16 - Kerala: Kerala is a state in southern India that is blessed with natural beauty and tranquility.
- Kerala is famous for its backwaters33, a network of canals, lakes, and rivers that offer scenic views and relaxing boat rides.
- Kerala also has lush green hills, tea plantations, spice gardens, wildlife sanctuaries, and beaches.
- Kerala is also known for its Ayurveda, a system of holistic medicine that originated in India.
17 - Varanasi: Varanasi is one of the oldest and holiest cities in India, located on the banks of the Ganges River.
- Varanasi is a sacred place for Hindus, who believe that dying here will liberate them from the cycle of rebirth.
- Varanasi is also a center of learning and culture, with many temples, ghats, ashrams, and festivals.
- Varanasi is a place where you can witness the essence of life and death.
18 - Ladakh: Ladakh is a region in northern India that borders Tibet and Pakistan.
- Ladakh is known for its stunning landscapes, high-altitude lakes, snow-capped mountains, and ancient monasteries.
- Ladakh is a paradise for adventure enthusiasts, who can enjoy trekking, biking, rafting, camping, and wildlife watching.
- Ladakh is also a place where you can experience the Tibetan culture and Buddhism.
- These some of the amazing places that India has to offer.
- India is a country that will surprise you, challenge you, inspire you, and enchant you.
- India is a country that you will never forget.
India Flag Population Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
India
- There are many landmarks in India that showcase the country’s rich and diverse culture, history, and heritage.
- Some of the landmarks in India that you might want to know more about are:
19 - Gateway of India: This is a 26-meter-high archway that was built in 1924 to commemorate the visit of King George V and Queen Mary to Mumbai.
- It is one of the most iconic symbols of Mumbai and India, and a popular spot for tourists and locals alike.
- The Gateway of India overlooks the Arabian Sea and offers a stunning view of the Taj Mahal Palace Hotel, which is another landmark in India.
20 - Qutub Minar: This is a 73-meter-high tower that was built in the 13th century by Qutub-ud-din Aibak, the founder of the Delhi Sultanate.
- It is the tallest brick minaret in the world and a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- The Qutub Minar is adorned with intricate carvings and inscriptions in Arabic and Sanskrit,
and is surrounded by other historical monuments such as the Quwwat-ul-Islam Mosque, the Iron Pillar, and the Alai Darwaza.
21 - Hawa Mahal: This is a five-story palace that was built in 1799 by Maharaja Sawai Pratap Singh as a part of the City Palace complex in Jaipur.
- It is also known as the Palace of Winds, because it has 953 windows that allow the breeze to flow through.
- The Hawa Mahal was designed to resemble the crown of Lord Krishna, and was used by the royal women to observe the street life without being seen.
22 - Khajuraho Temples: These are a group of Hindu and Jain temples that were built between the 10th and 12th centuries by the Chandela dynasty.
- They are famous for their erotic sculptures that depict various aspects of human life and sexuality.
- The Khajuraho Temples are also known for their architectural beauty and intricate details, and are considered as one of the finest examples of Indian art.
23 - Mysore Palace: This is a magnificent palace that was built in 1912 by Maharaja Krishnaraja Wodeyar IV as the official residence of the Wodeyar dynasty.
- It is one of the largest and most splendid palaces in India, and showcases a blend of Hindu, Islamic, Gothic, and Rajput styles.
- The Mysore Palace is also known for its grandeur and elegance, and its illumination with over 97,000 lights during festivals and special occasions.
India Flag Population Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- India is a country with many cities that have different characteristics, cultures, and attractions.
- Some of the cities in India that you might want to know more about are:
24 - Mumbai
- Mumbai: Mumbai is the financial capital and the most populous city in India.
- It is located on the west coast of India, along the Arabian Sea.
- Mumbai is a cosmopolitan city that offers a variety of experiences, from the glamorous Bollywood - industry to the historic colonial buildings.
- Mumbai is also known for its street food, nightlife, and shopping.
- Some of the popular tourist attractions in Mumbai are the Gateway of India, the Elephanta Caves, the Marine Drive, and the Haji Ali Dargah.
25 - Delhi
- Delhi: Delhi is the capital of India and a city that showcases the contrast between old and new.
- Delhi has many historical sites such as the Red Fort, the Qutub Minar, the Humayun’s Tomb, the Jama Masjid, and the Raj Ghat.
- Delhi also has modern attractions such as the Lotus Temple, the Akshardham Temple, the India Gate, and the Connaught Place.
- Delhi is also famous for its cuisine, culture, and festivals.
26 - Bangalore
- Bangalore: Bangalore is the IT hub and the third most populous city in India.
- It is located in the southern state of Karnataka, and is known as the Silicon Valley of India.
- Bangalore is a city that attracts many young professionals, entrepreneurs, and students with its opportunities, innovation, and education.
- Bangalore is also a city that offers a pleasant climate, green spaces, and nightlife.
- Some of the popular tourist attractions in Bangalore are the Lalbagh Botanical Garden, the Cubbon Park, the Bangalore Palace, and the Tipu Sultan’s Summer Palace.
27 - Hyderabad
- Hyderabad: Hyderabad is the capital of Telangana and a city that blends tradition and modernity.
- Hyderabad is famous for its pearls, biryani, and culture.
- Hyderabad is also a major center for biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and information technology.
- Hyderabad has many historical monuments such as the Charminar, the Golconda Fort, the Mecca Masjid, and the Chowmahalla Palace.
- Hyderabad also has some modern attractions such as the Hussain Sagar Lake, the Birla Mandir, and the Ramoji Film City.
28 - Kolkata
- Kolkata: Kolkata is the cultural capital and the fourth most populous city in India.
- It is located on the east coast of India, along the Hooghly River.
- Kolkata is a city that has a rich heritage, literature, art, and music.
- Kolkata is also known for its sweets, street food, and festivals.
- Some of the popular tourist attractions in Kolkata are the Victoria Memorial Hall, the Howrah Bridge, the Dakshineswar Kali Temple, and the Indian Museum.
- These some of the cities in India that you can explore and enjoy.
- India has many more cities that have their own charm and uniqueness.
- India is a country that will surprise you with its diversity and beauty.
India Flag Population Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- India has many beaches that offer a variety of experiences, from relaxation to adventure, from culture to nature.
- Some of the beaches in India that you might want to know more about are:
29 - Gokarna, Karnataka: Gokarna is a coastal town in Karnataka that is known for its pristine beaches and its spiritual significance.
- Gokarna is a pilgrimage site for Hindus, who come to visit the Mahabaleshwar Temple and perform rituals on the beach.
- Gokarna also attracts backpackers and hippies, who enjoy the laid-back vibe and the scenic views.
- Some of the popular beaches in Gokarna are Om Beach, Kudle Beach, Half Moon Beach, and Paradise Beach.
30 - Tarkarli, Maharashtra: Tarkarli is a village in Maharashtra that is famous for its clear blue water and white sand beaches.
- Tarkarli is a paradise for water sports enthusiasts, who can indulge in activities such as scuba diving, snorkeling, parasailing, jet skiing, and boating.
- Tarkarli also has a rich marine life, with coral reefs, dolphins, and turtles.
- Some of the popular beaches in Tarkarli are Tarkarli Beach, Devbagh Beach, Kolamb Beach, and Tsunami Island.
31 - Kaup, Karnataka: Kaup is a small town in Karnataka that is known for its lighthouse and its serene beaches.
- Kaup is a perfect place for a relaxing getaway, away from the crowds and the noise.
- Kaup also has a historical and cultural significance, as it was once ruled by the Alupas dynasty and has several temples and mosques.
- Some of the popular beaches in Kaup are Kaup Beach, Padukere Beach, Kodi Bengre Beach, and Udyavara Beach.
32 - Tharangambadi, Tamil Nadu: Tharangambadi is a former Danish colony in Tamil Nadu that is known for its heritage and its tranquil beaches.
- Tharangambadi means “the land of the singing waves” in Tamil, and it lives up to its name with its soothing sound of the sea.
- Tharangambadi also has a rich history, with monuments such as the Danish Fort, the Zion Church, the New Jerusalem Church, and the Masilamani Nathar Temple.
- Some of the popular beaches in Tharangambadi are Tharangambadi Beach, Akkarai Beach, Karaikal Beach, and Nagore Beach.
33 - Radhanagar, Andaman and Nicobar Islands: Radhanagar is a beach on Havelock Island in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands that is known for its beauty and its solitude.
- Radhanagar is often rated as one of the best beaches in Asia and the world by various travel magazines and websites.
- Radhanagar has a long stretch of white sand, turquoise water, lush green forest, and coral reefs.
- Radhanagar is ideal for swimming, sunbathing, snorkeling, and surfing.
- These some of the amazing beaches that India has to offer.
- India is a country that will surprise you with its diversity and beauty.
India Flag Population Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
34 - The climate of India is very diverse and complex, as it is influenced by various factors such as the Himalayas, the Thar Desert, the monsoon winds, and the latitude.
- India has six major climatic subtypes, according to the Köppen system:
- Arid deserts in the west, where the rainfall is very low and the temperature is very high.
- This region includes parts of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Punjab, and Haryana.
- Some of the cities in this region are Jodhpur, Jaipur, and Ahmedabad.
- Alpine tundra and glaciers in the north, where the altitude is very high and the temperature is very low.
- This region includes parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Sikkim.
- Some of the places in this region are Srinagar, Leh, Gangtok, and Nainital.
- Humid tropical regions supporting rain forests in the southwest and the island territories, where the rainfall is very high and the temperature is moderate to high.
- This region includes parts of Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Some of the places in this region are Thiruvananthapuram, Kochi, Chennai, and Port Blair.
- Subtropical humid regions in the north and northeast, where the rainfall is moderate to high and the temperature is moderate to high.
- This region includes parts of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Assam, and Odisha.
- Some of the places in this region are Lucknow, Patna, Kolkata, and Guwahati.
- Tropical wet and dry regions in the central and south-central parts of India, where the rainfall is moderate to low and the temperature is high.
- This region includes parts of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
- Some of the places in this region are Bhopal, Mumbai, Hyderabad, and Bangalore.
- Tropical savanna regions in the southeast coast of India, where the rainfall is moderate to low and the temperature is high.
- This region includes parts of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Odisha.
- Some of the places in this region are Kanyakumari, Visakhapatnam, Puri, and Pondicherry.
35 - India also has four seasons: winter (December to February),
summer or pre-monsoon (March to June),
monsoon or rainy (June to September),
and post-monsoon (October to November).
- The monsoon season is very important for India’s agriculture and economy, as it brings most of the annual rainfall.
- However, it can also cause floods and landslides in some areas.
- The winter season is generally dry and mild in most parts of India, except for some areas in the north where it can get cold and snowy.
- The summer season is generally hot and dry in most parts of India, except for some areas in the south where it can get humid.
- The post-monsoon season is generally warm and humid in most parts of India.
- India’s climate is also affected by tropical cyclones that can form in both the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
- They are more common from April to December, with two peaks before and after the monsoon (in May and October-November).
- The area most at risk is the northern part of the Bay of Bengal, where cyclones can cause heavy rain, strong winds, storm surges, and coastal erosion.
36 - India is a country that has a long and complex history of border relations with its neighboring countries.
- India shares land borders with seven countries: Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Afghanistan.
- India also shares maritime borders with three countries: Sri Lanka, Maldives, and Indonesia.
- Some of these borders are peaceful and open, while others are disputed and tense.
- some Details about India’s bordering countries:
37 - Pakistan: India and Pakistan have a 3,310-kilometer (2,060-mile) long border that was drawn by the British during the partition of India in 1947.
- The border is known as the Radcliffe Line, and it divides the states of Punjab and Kashmir between the two countries.
- The border is one of the most volatile in the world, as India and Pakistan have fought several wars and skirmishes over the Kashmir issue.
- The border is also the site of a daily flag ceremony at the Attari-Wagah crossing, where soldiers from both sides perform a display of patriotism and rivalry.
38 - China: India and China have a 3,488-kilometer (2,167-mile) long border that spans across the Himalayan mountains.
- The border is also known as the Line of Actual Control (LAC), and it is not clearly demarcated or agreed upon by both countries.
- The border is the source of a longstanding territorial dispute that led to a war in 1962 and several clashes since then.
- The border is also the site of frequent standoffs and face-offs between the Indian and Chinese troops,
especially in the regions of Ladakh, Arunachal Pradesh, and Sikkim.
39 - Nepal: India and Nepal have a 1,752-kilometer (1,089-mile) long border that runs along the foothills of the Himalayas.
- The border is an open one, which means that citizens of both countries can cross it without any visa or passport.
- The border is also a cultural and economic link between the two countries,
as many Nepalis work and study in India, and many Indians visit Nepal for tourism and pilgrimage.
- The border is also a source of some disputes, such as the ones over the Kalapani and Susta territories.
40 - Bhutan: India and Bhutan have a 578-kilometer (359-mile) long border that connects the Indian states of West Bengal, Sikkim, Assam,
and Arunachal Pradesh with the Bhutanese districts of Samdrup Jongkhar, Trashigang, Mongar,
Pemagatshel, Samtse, Chukha, Haa, Paro, Thimphu, Punakha, Wangdue Phodrang, Trongsa, Bumthang, Zhemgang, Sarpang, Dagana, Tsirang.
- The border is a friendly one, as India and Bhutan have a special relationship based on mutual trust and cooperation.
- India provides economic and military assistance to Bhutan, while Bhutan supports India’s interests in regional and international forums.
41 - Bangladesh: India and Bangladesh have a 4,096-kilometer (2,545-mile) long border that is the fifth-longest in the world.
- The border was established after the independence of Bangladesh from Pakistan in 1971.
- The border is also one of the most complex in the world, as it has many enclaves (territories surrounded by another country)
and exclaves (territories separated from their own country by another country).
- In 2015, India and Bangladesh exchanged 162 enclaves to simplify their border management and improve the lives of their residents.
42 - Myanmar: India and Myanmar have a 1,643-kilometer (1,021-mile) long border that connects the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh.
India Flag Population Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism History

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
National Anthem of India
- Details
- Written by: Elmazen
- Category: Flags of Countries of the World
- Hits: 1706
Laos
Laos: A Land of Natural and Cultural Wonders
1 - Laos is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, bordered by Myanmar, China, Vietnam, Cambodia, and Thailand.
It is one of the few remaining communist countries in the world, but also one of the most diverse and fascinating destinations for travelers.
Laos Flag Population History Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism
Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
Laos has a rich and ancient history, a vibrant and colorful culture, and a stunning natural beauty that will leave you breathless.
2 - Laos has a population of about 7.6 million people, according to the United Nations data in 2021.
The majority of the population are ethnic Lao, who follow Theravada Buddhism and speak Lao, the official language.
However, there are also many other ethnic groups in Laos, such as the Hmong, Khmu, Tai, Mon-Khmer, and Chinese, who have their own languages, customs, and traditions.
Laos is a multiethnic and multilingual country that celebrates its diversity and harmony.
3 - Laos has a long and complex history that dates back to the first millennium BC.
The earliest known civilization in Laos was the Funan Kingdom, which was influenced by Indian culture and religion.
Later, the Chenla Kingdom emerged as a successor of Funan, and expanded its territory and power in the region.
In the 14th century, the Lan Xang Kingdom was founded by King Fa Ngum, who unified the various Lao principalities under his rule.
Lan Xang means “million elephants and white parasol”, which are the traditional symbols of Laos.
The Lan Xang Kingdom was one of the most powerful and prosperous kingdoms in Southeast Asia,
until it split into three rival kingdoms in the 18th century: Luang Prabang, Vientiane, and Champasak.
In the 19th century, Laos became a part of French Indochina, along with Vietnam and Cambodia.
The French colonized and exploited Laos for its natural resources, such as rubber, tin, and coffee.
They also introduced Christianity, French language, and Western education to some segments of the Lao society.
However, they also faced resistance from the Lao nationalist movements, such as the Lao Issara (Free Laos) and the Pathet Lao (Lao Nation).
During World War II, Laos was occupied by Japan, which declared its independence from France.
After the war, Laos became a constitutional monarchy under King Sisavang Vong,
but also a battleground for the First Indochina War (1946-1954) and the Second Indochina War (1955-1975), also known as the Vietnam War.
These wars caused immense suffering and devastation to Laos, as it was bombed heavily by the US forces and invaded by the North Vietnamese troops.
In 1975, after the fall of Saigon, the Pathet Lao took over the country and established the Lao People’s Democratic Republic (Lao PDR),
a socialist state allied with Vietnam and the Soviet Union.
Since then, Laos has undergone economic and political reforms to integrate into the global market and society.
It has opened up to foreign trade and investment, especially in the sectors of hydropower, mining, tourism, and agriculture.
It has also improved its relations with its neighbors and joined regional and international organizations,
such as ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) in 1997 and WTO (World Trade Organization) in 2013.
However, Laos still faces many challenges and issues, such as poverty, inequality, corruption, human rights violations, environmental degradation, and public debt.
4 - The capital of Laos is Vientiane, which is located on the banks of the Mekong River near the border with Thailand.
Vientiane is a city that combines old and new elements: ancient temples and monuments coexist with modern buildings and infrastructure.
Laos Flag Population History Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- Some of the most famous attractions in Vientiane are:
5 - Pha That Luang: The national symbol of Laos, this golden stupa is believed to contain a relic of Buddha’s breastbone.
It was built in the 16th century by King Setthathirath on the site of an earlier Khmer temple.
6 - Patuxai: A monumental arch that resembles the Arc de Triomphe in Paris,
this structure was built in 1968 to commemorate those who died fighting for Laos’s independence from France.
It is decorated with Lao motifs and sculptures.
7 - Wat Si Saket: The oldest temple in Vientiane, this Buddhist temple was built in 1818 by King Anouvong.
It features a cloister wall with thousands of Buddha images and statues.
8 - Talat Sao: The morning market, this complex is a popular place for shopping and eating.
You can find various goods here, such as clothes, electronics, jewelry, handicrafts, souvenirs, food, and more.
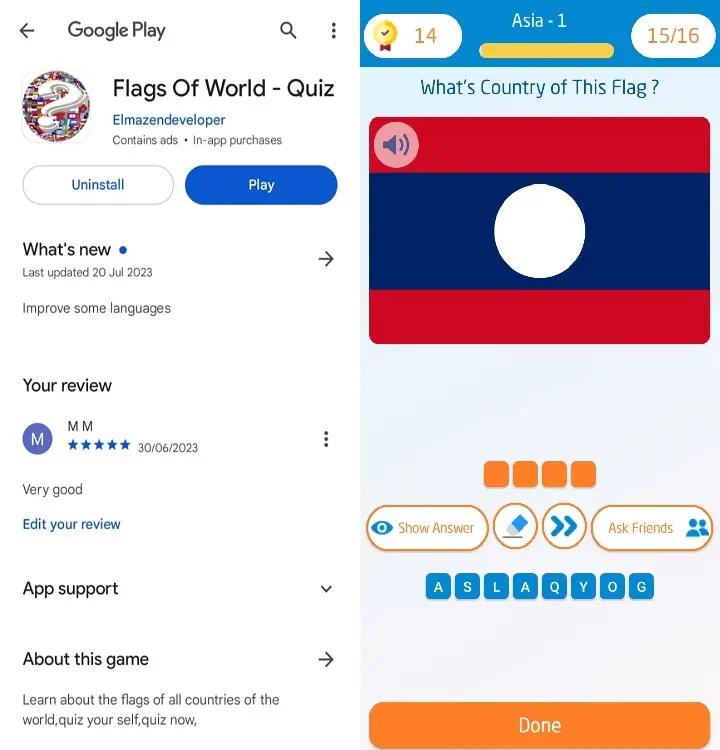
9 - The flag of Laos consists of three horizontal stripes: red on top and bottom, and blue in the middle.
The blue stripe is twice the height of the red stripes.
In the center of the flag, there is a white disk that symbolizes the unity of the Lao people and the moon over the Mekong River.
The red stripes stand for the blood shed by the Lao people in their struggle for freedom and independence.
The blue stripe represents the Mekong River and the country’s wealth.
The flag was adopted on December 2, 1975, based on the Pathet Lao political party.
10 - Laos belongs to the continent of Asia, specifically to the subregion of Southeast Asia.
It is situated on the Indochinese Peninsula, which is a landmass that lies between the Indian Ocean and the South China Sea.
11 - Laos shares borders with five other countries:
Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and southwest.
Laos has a total area of about 236,800 square kilometers (91,400 square miles), making it slightly larger than Utah or Romania.
12 - Laos has a tropical monsoon climate, with two distinct seasons: wet and dry.
The wet season lasts from May to October, when most of the rainfall occurs.
The dry season lasts from November to April, when temperatures are cooler and drier.
13 - Laos has a lower-middle income developing economy that has undergone economic restructuring to integrate into the globalized world market.
The Lao government has implemented market-based economic practices while maintaining a high degree of state control and welcoming foreign direct investment.
The Lao economy has grown at nearly 8% for most of the last decade, but remains dependent on external demand for its natural resources.
The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in a slowdown of the Lao economy, with a growth rate of just 0.5% in 2020 and a forecasted growth rate of 2.5% in 2022.
The main sectors of the Lao economy are agriculture, industry, and services.
Agriculture accounts for about 16% of GDP and employs about 70% of the labor force.
The main crops are rice, corn, cassava, coffee, sugarcane, rubber, and tobacco.
Industry accounts for about 33% of GDP and employs about 10% of the labor force.
The main industries are mining, hydropower, construction, manufacturing, and tourism.
Services account for about 41% of GDP and employ about 20% of the labor force.
The main services are trade, transport, communication, finance, education, health, and public administration.
14 - The currency of Laos is the kip (LAK), which is divided into 100 atts.
However, due to inflation and devaluation, coins are no longer used and atts are worthless.
Banknotes are issued in denominations of 500, 1,000, 2,000, 5,000, 10,000, 20,000, 50,000, and 100,000 kips.
The exchange rate as of 11 October 2023 is about 20,475 kips per US dollar.
15 - The country code for Laos is +856, which means that you need to dial this number before the local phone number when calling from another country.
For example, if you want to call a landline in Vientiane from the US or Canada, you need to dial: 011 + 856 + 21 + ??? ??? (where ??? ??? is the local phone number).
If you want to call a mobile phone in Laos from another country, you need to dial: 011 + 856 + 20 or 30 + ??? ??? (where ??? ??? is the mobile phone number).
16 - The correct way to pronounce Laos is "lah-ohs", with a short “a” sound as in “law” and a long “o” sound as in “goose”.
While some people may mispronounce it as “lay-ohs” or “lee-ohs”, these are incorrect and should be avoided.
The name Laos comes from the French transcription of the word Lao, which is the name of the dominant ethnic group and language in the country.
Laos Flag Population History Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
17 - The abbreviation for Laos is LAO, which is also its ISO 3166-1 alpha-3 code.
This code is used for international identification purposes, such as in passports, vehicle registration plates, and internet domains.
For example, the top-level domain for Laos is .la.
18 - The culture of Laos is influenced by its geography, history, religion, and ethnic diversity.
Laos is a land of mountains, forests, rivers, and waterfalls, which have shaped its natural beauty and biodiversity.
- Laos has many landmarks that showcase its natural and cultural beauty.
Some of the most popular and impressive landmarks are:
19 - Kuang Si Falls: A stunning three-tiered waterfall that flows into a turquoise pool.
You can swim, hike, or picnic here and enjoy the scenery.
Kuang Si Falls is located about 29 kilometers south of Luang Prabang.
20 - Buddha Park: A collection of over 200 Buddhist and Hindu statues and sculptures.
The park was created by a monk who wanted to spread his teachings and art. Buddha Park is located about 25 kilometers southeast of Vientiane.
21 - Mount Phousi: A sacred hill that offers panoramic views of Luang Prabang and the Mekong River.
You can climb the 355 steps to the top and visit the temples and shrines along the way.
Mount Phousi is located in the center of Luang Prabang.
22 - Pha That Luang: The national symbol of Laos, this golden stupa is believed to contain a relic of Buddha’s breastbone.
It was built in the 16th century by King Setthathirath on the site of an earlier Khmer temple.
Pha That Luang is located about 4 kilometers northeast of Vientiane.
23 - Wat Phou: An ancient Khmer temple complex that dates back to the 5th century.
The temple is dedicated to Shiva and features elaborate carvings, statues, and terraces.
Wat Phou is located about 45 kilometers south of Pakse.
- Laos is a country that has many cities with different characteristics and attractions.
cities in Laos are:
Vientiane
24 - Vientiane: The capital and largest city of Laos, Vientiane is located on the banks of the Mekong River near the border with Thailand.
Vientiane is a city that combines old and new elements: ancient temples and monuments coexist with modern buildings and infrastructure.
Some of the most famous attractions in Vientiane are Pha That Luang,
the national symbol of Laos; Patuxai, a monumental arch that resembles the Arc de Triomphe in Paris;
25 - Wat Si Saket, the oldest temple in Vientiane; and Talat Sao, the morning market.
Savannakhet
26 - Savannakhet: The second largest and second most populous city in Laos, Savannakhet is the capital of Savannakhet Province.
Savannakhet is a city that has a rich cultural and historical heritage, as it was once a part of the Khmer Empire, the Lan Xang Kingdom, and French Indochina.
Some of the most famous attractions in Savannakhet are That Ing Hang,
a 16th-century stupa that is one of the most sacred sites in Laos;
Savannakhet Historic City, a well-preserved area that showcases colonial architecture and traditional Lao houses;
and Dinosaur Museum, a museum that displays fossils and skeletons of dinosaurs found in the region.
Pakse
27 - Pakse: The third largest and third most populous city in Laos, Pakse is the capital of Champasak Province.
Pakse is a city that is a gateway to many natural and cultural wonders,
as it is situated near the Mekong River, the Bolaven Plateau, and the ancient Khmer temple complex of Wat Phou.
Some of the most famous attractions in Pakse are Wat Luang,
the main temple of Pakse that features a large Buddha statue; Champasak Historical Heritage Museum,
a museum that exhibits artifacts and information about the history and culture of Champasak;
and Dao Heuang Market, the largest market in southern Laos that sells various goods and products.
Luang Prabang
28 - Luang Prabang: The fourth largest and fourth most populous city in Laos, Luang Prabang is the capital of Luang Prabang Province.
Luang Prabang is a city that is a UNESCO World Heritage Site,
as it is considered to be one of the best-preserved examples of the fusion of traditional Lao and colonial French architecture.
Some of the most famous attractions in Luang Prabang are Wat Xieng Thong,
the most beautiful and ornate temple in Luang Prabang; Royal Palace Museum,
a former royal residence that displays royal artifacts and paintings; Kuang Si Falls,
a stunning three-tiered waterfall that flows into a turquoise pool; and Mount Phousi, a sacred hill that offers panoramic views of Luang Prabang and the Mekong River.
- Laos is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, which means that it does not have any coastline or beaches.
However, that does not mean that you cannot enjoy the sun and water in Laos.
There are many alternatives to beaches in Laos, such as islands, rivers, lakes, waterfalls, and pools.
- Here are some of the best beach alternatives in Laos that you can visit:
29 - Don Daeng Island: This is a sleepy, atmospheric island located in the middle of the Mekong River in Southern Laos.
You can relax on the sandy banks of the river, swim in the clear water, or cycle around the island and explore the rural villages and rice fields.
Don Daeng Island is also close to Wat Phou, an ancient Khmer temple complex that is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
30 - Muang La: This is a small town in Northern Laos that is surrounded by lush mountains and forests.
You can soak in the natural hot springs that are located near the Nam Pak River, or enjoy the infinity pool at the Muang La Resort that overlooks the scenic landscape.
Muang La is also a good base for trekking to ethnic minority villages and experiencing their culture.
31 - 4000 Islands: This is a region in Laos where the Mekong River expands into a wide archipelago and the water slows.
You can choose from one of the many islands to stay on, such as Don Khong, Don Det, or Don Khone.
You can enjoy activities such as kayaking, tubing, fishing, or watching the rare Irrawaddy dolphins.
You can also visit the impressive Khone Phapheng Falls, which are the largest waterfalls in Southeast Asia.
Laos Flag Population History Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
32 - The climate of Laos is mainly tropical, with variations depending on the altitude, latitude, and monsoon influence.
Laos has two distinct seasons: the rainy season and the dry season.
The rainy season lasts from May to October, when the southwest monsoon brings heavy rainfall and high humidity to most of the country.
The dry season lasts from November to April, when the northeast monsoon brings cooler and drier air to most of the country.
However, the dry season can be divided into two sub-seasons: the cool dry season from November to February, and the hot dry season from March to April.
The average annual temperature in Laos is about 26°C (79°F), but it can vary from 14°C (57°F) in the northern mountains to 34°C (93°F) in the southern plains.
The average annual rainfall in Laos is about 1,700 mm (67 in),
but it can range from 1,000 mm (39 in) in the north-central region to 3,000 mm (118 in) in the south-eastern region.
The Mekong River, which flows through Laos from north to south, moderates the climate and provides water for agriculture and hydroelectricity.
33 - The best time to visit Laos depends on your preferences and activities.
Generally, the cool dry season from November to February is considered the most pleasant and popular time to visit Laos,
as the weather is mild and sunny, and the landscape is green and lush.
However, this is also the peak tourist season, so you may encounter higher prices and crowds.
The hot dry season from March to April is less favorable, as the weather is very hot and dusty, and the air quality is poor due to slash-and-burn agriculture.
The rainy season from May to October is less crowded and cheaper, but also wetter and more humid.
However, some people may enjoy the rainforest scenery and the waterfalls during this time.
You should also be aware of the risk of flooding, landslides, and tropical storms during this time.
Laos Flag Population History Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- Laos is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, which means that it does not have any coastline or beaches.
However, it has many neighbors that share its borders.
34 - Laos is bordered by five countries: Myanmar, China, Vietnam, Cambodia, and Thailand.
The total length of the land borders of Laos is about 5,083 kilometers (3,158 miles).
The border between Laos and Myanmar is about 238 kilometers (148 miles) long and runs along the northwestern edge of Laos.
The border follows the Mekong River for a short distance and then crosses the mountainous terrain of the Luang Namtha Province.
The border was established by the French colonial authorities in the late 19th century and has been disputed by both countries in the past.
The border between Laos and China is about 423 kilometers (263 miles) long and runs along the northern edge of Laos.
The border follows the crest of the Annamite Range, which separates the Mekong River basin from the Red River basin.
The border was demarcated by a treaty signed in 1991 and ratified in 1994 by both countries.
The border between Laos and Vietnam is about 2,161 kilometers (1,343 miles) long and runs along the eastern edge of Laos.
The border follows the Annamite Range for most of its length, except for a section in the south where it deviates to the east.
The border was defined by several agreements between France and Vietnam in the late 19th and early 20th centuries,
but was not fully demarcated until 2007-2008 by both countries.
The border between Laos and Cambodia is about 541 kilometers (336 miles) long and runs along the southeastern edge of Laos.
The border follows the Mekong River for a short distance and then crosses the hilly terrain of the Attapeu and Champasak Provinces.
The border was determined by a treaty signed in 1904 between France and Siam (now Thailand), but was not fully demarcated until 2019-2020 by both countries.
The border between Laos and Thailand is about 1,720 kilometers (1,069 miles) long and runs along the southwestern and western edge of Laos.
The border follows the Mekong River for most of its length, except for a section in the north where it crosses the mountainous terrain of the Xaignabouli Province.
The border was established by several treaties signed between France and Siam in the late 19th and early 20th centuries,
but has been disputed by both countries over some islands in the river.
- Laos has five bridges that connect it with its neighboring countries.
- These are:
35 - The First Thai–Lao Friendship Bridge: This bridge links Vientiane in Laos with Nong Khai in Thailand over the Mekong River.
It was opened in 1994 with Australian aid.
36 - The Second Thai–Lao Friendship Bridge: This bridge links Savannakhet in Laos with Mukdahan in Thailand over the Mekong River.
It was opened in 2006 with Japanese aid.
37 - The Third Thai–Lao Friendship Bridge: This bridge links Khammouane in Laos with Nakhon Phanom in Thailand over the Mekong River.
It was opened in 2011 with Japanese aid.
38 - The Fourth Thai–Lao Friendship Bridge: This bridge links Bokeo in Laos with Chiang Rai in Thailand over the Mekong River.
It was opened in 2013 with Chinese aid.
39 - The Sino–Lao Railway Bridge: This bridge links Luang Namtha in Laos with Yunnan in China over the Namtha River.
It is part of the Kunming–Singapore Railway project and was completed in 2020 with Chinese aid.
Laos Flag Population History Landmarks Currency Cities Tourism

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
National Anthem of Laos
- Details
- Written by: Elmazen
- Category: Flags of Countries of the World
- Hits: 12135
Kuwait
Kuwait: A Country of Rich History and Culture
1 - Kuwait is a small country in Western Asia, located on the northern tip of the Persian Gulf.
2 - It shares borders with Iraq and Saudi Arabia, and has a coastline of about 499 km.
Kuwait Flag Tourism Population History Landmarks Currency Cities

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
3 - Kuwait is one of the richest countries in the world, thanks to its abundant oil reserves and strategic location.
It is also a country of rich history and culture, with a diverse and tolerant society.
4 - Kuwait’s history dates back to ancient times, when it was part of the Mesopotamian civilization.
It was later colonized by the Greeks, the Persians, and the Romans, before becoming part of the Islamic world in the 7th century.
Kuwait emerged as an independent sheikhdom in the 18th century, under the rule of the Al Sabah dynasty, which still governs the country today.
Kuwait was a prosperous trading port, connecting Asia, Africa, and Europe.
It also played a significant role in the pearl industry, until the discovery of oil in the 20th century.
- Kuwait became a British protectorate in 1899, and gained its independence in 1961.
However, it faced several challenges and conflicts in the following decades,
such as the Iran-Iraq War, the Iraqi invasion and occupation in 1990-1991, and the Gulf War.
Kuwait was able to overcome these difficulties with the help of its allies, especially the United States and other Arab countries.
Kuwait also embarked on a process of political and economic reforms, aiming to diversify its economy and enhance its democracy.
5 - Kuwait’s capital and largest city is Kuwait City, which is home to about 2.4 million people.
Kuwait City is a modern and cosmopolitan metropolis, with skyscrapers, shopping malls, museums, parks, and mosques.
It also has many historical and cultural attractions, such as the Kuwait Towers, the Grand Mosque,
the Seif Palace, the Tareq Rajab Museum, and the Souq Mubarakiya.
Kuwait City is also a hub for education, media, finance, and commerce in the region.
6 - Kuwait’s currency is the Kuwaiti dinar (KWD), which is the highest-valued currency in the world.
One dinar is divided into 1000 fils.
The dinar was introduced in 1961, replacing the Gulf rupee that was used during the British rule.
The dinar is pegged to a basket of currencies, mainly the US dollar.
The dinar’s value reflects Kuwait’s economic strength and stability.
7 - Kuwait’s country code is +965, which is used to make international phone calls to or from Kuwait.
The country code is followed by an eight-digit local number, starting with 2 for landlines and 5 or 6 for mobile phones.
For example, to call a landline number in Kuwait City from abroad, you would dial +965 2??? ???.
To call a mobile number in Kuwait from abroad, you would dial +965 5??? ??? or +965 6??? ???.
To pronounce Kuwait correctly, you can say “koo-WAIT”, with the stress on the first syllable.
Kuwait Flag Tourism Population History Landmarks Currency Cities

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
8 - Kuwait’s country abbreviation is KW or KWT, which is used to identify Kuwait in various contexts,
such as international organizations, sports events, internet domains, postal codes, and license plates.
For example, Kuwait is a member of the United Nations (UN), the Arab League (AL),
the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
Kuwait also participates in the Olympic Games (IOC code: KUW), the Asian Games (OCA code: KUW), and the FIFA World Cup (FIFA code: KUW).
Kuwait’s internet domain is .kw or .كويت (in Arabic script), and its postal code format is five digits (e.g., 13001).
Kuwait’s license plates consist of three Arabic numerals followed by three Arabic letters (e.g., 123 ABC).
9 - Kuwait’s culture is influenced by its Islamic faith, Arab heritage, Bedouin traditions, and cosmopolitan outlook.
Kuwaitis are known for their hospitality, generosity, tolerance, and patriotism.
They value family ties, social bonds, education, art, and music.
They also enjoy various festivals and celebrations throughout the year,
such as Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, National Day (February 25), Liberation Day (February 26), Hala February (a month-long cultural festival),
Ramadan (the holy month of fasting), and Gargee’an (a mid-Ramadan celebration for children).
- Kuwait’s best places to visit include:
10 - The Scientific Center: A cultural and educational facility that features an aquarium, a planetarium, a discovery place for children, and an IMAX theater.
11 - Al Shaheed Park: A large urban park that offers green spaces, walking trails, fountains, museums, and cultural events.
12 - Sadu House: A museum and cultural center that showcases the traditional art of Bedouin weaving and embroidery.
13 - Kuwait Towers: A landmark and symbol of Kuwait, consisting of three towers that serve as a water reservoir, a restaurant, and a viewing platform.
14 - Mirror House: A unique and artistic house that is covered with mirrors inside and outside, creating a dazzling and surreal effect.
15 - Dar Al Athar Al Islamiyya: A cultural organization that displays a collection of Islamic art and artifacts from different regions and periods.
- Kuwait has many landmarks that reflect its history, culture, and modernity.
Some of the most famous landmarks are:
16 - The Grand Mosque of Kuwait: This is the largest and most prominent mosque in Kuwait, covering an area of 45,000 square meters.
It can accommodate up to 10,000 worshippers at a time.
The mosque was built between 1979 and 1986, with a blend of traditional Islamic and modern architecture.
The mosque has a stunning interior, decorated with marble, wood, and gold.
It also has a library that contains more than 20,000 books and manuscripts on Islamic topics.
The mosque is open to visitors of all faiths, who can join free guided tours.
They are located on the Arabian Gulf road, overlooking the sea.
They were designed by a Swedish architect and completed in 1979.
The towers have a distinctive spherical shape, covered with blue-green tiles that reflect the sun and the water.
The main tower is 187 meters high and has two spheres.
The lower sphere contains a rotating restaurant that offers panoramic views of the city.
The upper sphere contains a viewing gallery that can be reached by an elevator.
The second tower is 147 meters high and holds one million gallons of water.
The third tower is 113 meters high and provides electricity and lighting for the other two towers.
17 - Kuwait National Museum: This is the official museum of Kuwait, located next to the National Assembly building.
It was established in 1983 and consists of four buildings that house different collections and exhibits.
The museum showcases the history, culture, and art of Kuwait from ancient times to the present day.
It also has a planetarium that offers educational shows about astronomy and space exploration.
The museum was severely damaged during the Iraqi invasion in 1990-1991, but it was restored and reopened in 2000.
18 - Souk Al-Mubarakiya: This is one of the oldest and most popular markets in Kuwait, located in the heart of the city.
It dates back to more than 200 years ago, when it was a major trading center for merchants from across the region.
The souk retains its traditional charm and atmosphere, with narrow alleys, wooden shops, and colorful goods.
You can find everything from spices, perfumes, textiles, jewelry, antiques, handicrafts, to fresh fruits, vegetables, meat, and fish.
The souk also has many cafes and restaurants that serve authentic Kuwaiti cuisine.
Kuwait Flag Tourism Population History Landmarks Currency Cities

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- Kuwait is a country that has many cities, each with its own characteristics and attractions.
Some of the most notable cities in Kuwait are:
19 - Kuwait City: This is the capital and largest city of Kuwait, located on the southern shores of Kuwait Bay on the Persian Gulf.
Kuwait City is the country’s political, cultural, and economic center, with skyscrapers, shopping malls, museums, parks, and mosques.
It also has many historical and cultural attractions, such as the Kuwait Towers, the Grand Mosque, the Seif Palace, the Tareq Rajab Museum, and the Souq Mubarakiya.
20 - Al Ahmadi: This is the most populated city in Kuwait, with a population of 637,411 people.
It is located along Kuwait’s eastern coastline and serves as the capital of the Al Ahmadi Province.
This city is relatively young, founded in 1946 after the discovery of oil.
The first immigrants to live here were British and Indian.
City planners based its design on American urban areas.
Headquarters for the Kuwait Oil Company and the Kuwait National Petroleum Company are located here.
The biggest industry here is oil refinery. The city is known for being the greenest city in Kuwait.
21 - Hawalli: This is the second most populated urban area in Kuwait, with a population of 164,212 people.
It is one of the several areas that make up the Hawalli Governorate and is located about 8 km from Kuwait City.
During and after the Gulf War, many of the city’s Palestinian residents left.
Today, it is home to a large Arab population.
This city is home to two international schools, the American School of Kuwait and the New Pakistan International School.
Additionally, the Qadsia football stadium is located here, which is the most important in Kuwait.
Hawalli is a large commercial center with a large mall and several types of stores.
22 - Al Farwaniyah: This is the third most populated area in Kuwait, with a population of 86,525 people.
It is located in the Farwaniyah Governorate, the most populous in the country, and about 10 km from Kuwait City.
Al Farwaniyah is one of the major residential areas of Kuwait and houses the largest number of foreign immigrants.
Men far outnumber women here, which is true of the entire country.
23 - Al Jahra: This is a city and an oasis in western Kuwait, with a population of 24,281 people.
It is located about 50 km from Kuwait City and serves as the capital of the Al Jahra Governorate.
Al Jahra has a long history as a farming community and a strategic location on trade routes.
It was also the site of several battles between Kuwait and its enemies,
such as the Battle of Jahra in 1920 against Saudi Arabia and the Battle of Al Jahra in 1990 against Iraq.
Al Jahra has several attractions, such as the Red Palace Museum, the Jahra Copthorne Hotel and Resort, and the Jahra Nature Reserve.
These are some of the cities in Kuwait.
Kuwait Flag Tourism Population History Landmarks Currency Cities

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
- Kuwait is a country that has many beaches, both public and private, that offer a variety of activities and amenities for visitors.
Some of the most popular beaches in Kuwait are:
24 - Messilah Beach: This is a private beach located in Salmiya, Kuwait, that is part of the Jumeirah Messilah Beach Hotel & Spa.
The beach has a long stretch of sand, clear water, and a view of the Kuwait Towers.
The beach also has a swimming pool, a kids’ club, a spa, and several restaurants and cafes.
The beach is open to hotel guests and visitors who pay an entrance.
25 - Al Khiran Beach: This is a resort with artificial canals, located in the south of Kuwait.
The resort has a marina, a mall, a park, and several hotels and chalets.
The beach is sandy and shallow, suitable for families and children.
The beach also offers water sports, such as jet skiing, kayaking, and sailing.
26 - Egaila Beach: This is a private beach in Kuwait, famous as a seaside spot for picnics and BBQ.
The beach has fine sand and pebbles, and the water is calm and clear.
The beach also has a playground, a volleyball court, and a basketball court.
The beach is open to visitors who pay an entrance fee.
27 - Al Kout Beach: This is a public beach in Kuwait, located next to the Al Kout Mall and the Al Kout Beach Hotel.
The beach is comfortable and nice for a stroll, but it can get crowded on weekends.
The beach also has a basketball court, a fountain show, and several cafes and restaurants.
28 - Hilton Beach Resort: This is a beachfront resort in Kuwait, located on the Arabian Gulf Road.
The resort has direct access to a beautiful private sandy beach, where guests can relax under the beach umbrellas, enjoy cold beverages, and swim in the clear water.
The resort also has a swimming pool, a spa, a fitness center, and several dining options.
29 - Fintas Beach: This is a public beach in Kuwait, located in the Fintas area.
The beach has smooth entry into the water, but with a lot of stones on the bottom.
The beach also has palm trees, benches, and trash bins.
The beach is popular among locals and expats who like to fish or camp on the shore.
30 - Mangaf Beach: This is a city beach in the southern suburbs of Kuwait City.
The beach has fine sand and good entry into the water.
However, the beach can be dirty and polluted due to its proximity to industrial areas.
The beach also has some cafes and restaurants nearby.
31 - Marina Beach: This is a city beach in Kuwait, mainly popular among foreign workers.
The beach has clean sand and water, and a view of the Marina Mall and the Marina Crescent.
The beach also has some facilities, such as showers, changing rooms, toilets, and sunbeds.
The beach is open to visitors who pay an entrance fee.
These are some of the beaches in Kuwait.
32 - Kuwait is a country that has a very hot and dry climate, with little rainfall and high temperatures throughout the year.
The climate is influenced by the desert conditions, the Persian Gulf, and the seasonal winds.
Here are some more facts about the climate in Kuwait:
Kuwait has a hyper arid desert climate that is highly variable with recurrent extremes.
Much of Kuwait is characterized by loose, mobile surface sediments that have very low levels of nutrients and organic matter.
Kuwait has four seasons: winter, spring, summer, and autumn.
Winter lasts from December to February, and is very mild, with average temperatures ranging from 8.5 to 19.5 °C (47 to 67 °F).
Spring lasts from March to May, and is sunny and warm, with average temperatures ranging from 14 to 40.9 °C (57 to 106 °F).
Summer lasts from June to September, and is scorchingly hot and windy, with average temperatures ranging from 28.9 to 46.9 °C (84 to 116 °F).
Autumn lasts from October to November, and is still hot and sunny, with average temperatures ranging from 14.5 to 36.6 °C (58 to 98 °F).
Kuwait receives very little rainfall, slightly higher than 100 millimeters (4 inches) per year.
Rainfall occurs mainly from November to April, in the form of rare showers, which can sometimes be so intense and concentrated as to cause flooding.
The wettest month is July, with an average of 18 mm (0.72 inches) of rain.
The driest month is June, with an average of 0 mm (0 inches) of rain.
Kuwait has a lot of sunshine throughout the year, with an average of about 9 hours of sunshine per day.
The sunniest month is June, with an average of 12 hours of sunshine per day.
The least sunny month is December, with an average of 6 hours of sunshine per day4.
Kuwait has a low relative humidity, which often falls below 10%.
The most humid month is December, with an average relative humidity of 58%.
The least humid month is June, with an average relative humidity of 15%.
Kuwait has a moderate wind speed, which can vary depending on the season and the direction.
The windiest month is June, with an average wind speed of 19 km/h (12 mph).
The calmest month is October, with an average wind speed of 13 km/h (8 mph).
The wind can blow from different directions, such as the north-western shamal wind,
which brings dust storms and cooler temperatures; the south-eastern sharqi wind,
which brings hot and humid air; and the south-western jili wind, which brings very hot and dry air.
Kuwait has a high evaporation rate, which exceeds the rainfall by more than ten times.
This means that the soil moisture is very low and the groundwater resources are scarce.
Kuwait has a high variation in temperature between day and night, especially in summer.
The diurnal temperature range can be as high as 20 °C (36 °F) or more.
Kuwait has a high variation in temperature between seasons, especially between summer and winter.
The annual temperature range can be as high as 38 °C (68 °F) or more.
These are some of the aspects of the climate in Kuwait.
Kuwait Flag Tourism Population History Landmarks Currency Cities

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,
Kuwait
33 - Kuwait is a country that has two land borders and three maritime borders with other countries.
The land borders are with Iraq and Saudi Arabia, and the maritime borders are with Iran, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia.
Here are some more details about Kuwait’s country borders:
The border with Iraq is about 254 km (158 mi) long and runs from the tripoint with Saudi Arabia in the south to the Persian Gulf in the north.
The border was established by the Anglo-Ottoman Convention of 1913, which defined Kuwait as an autonomous region within the Ottoman Empire.
However, Iraq did not recognize Kuwait’s independence in 1961 and claimed Kuwait as part of its territory.
Iraq invaded Kuwait in 1990, but was expelled by a US-led coalition in 1991.
The border was demarcated by a UN commission in 1992, based on the 1963 agreement between Kuwait and Iraq.
The border with Saudi Arabia is about 222 km (138 mi) long and runs from the Persian Gulf in the east to the tripoint with Iraq in the west.
The border was set by the Treaty of Al Uqayr in 1922, which also created a neutral zone between the two countries.
The neutral zone was divided into two parts in 1966, and each part was administered by one country.
The division was finalized in 1969, after the discovery of oil in the area.
The oil resources are shared equally between Kuwait and Saudi Arabia.
The maritime border with Iran is about 200 km (124 mi) long and runs along the median line of the Persian Gulf.
The border was agreed upon by Kuwait and Iran in 1965, following the principles of international law.
The border delimits the territorial waters and the exclusive economic zones of both countries, where they have sovereign rights over natural resources.
The maritime border with Iraq is about 36 km (22 mi) long and runs along the median line of the Khawr Abd Allah waterway.
The border was determined by the UN commission in 1993, as part of the demarcation of the land border between Kuwait and Iraq.
The border defines the territorial waters and the fishing rights of both countries.
The maritime border with Saudi Arabia is about 105 km (65 mi) long and runs along the median line of the Persian Gulf.
The border was agreed upon by Kuwait and Saudi Arabia in 1965, along with the maritime border with Iran.
The border delimits the territorial waters and the exclusive economic zones of both countries, where they have sovereign rights over natural resources.
Kuwait Flag Tourism Population History Landmarks Currency Cities

Download the application  Flags Of World - Quiz ,
Flags Of World - Quiz ,
and test your knowledge with Flags of World ,